SPIRAL DYNAMICS
DEVELOPMENTAL LEVELS
DON BECK, CHRISTOPHER COWAN, CLARE GRAVES
Website by AntDX316
Overview
Spiral Dynamics is a model of the evolutionary development of individuals, organizations, and societies. It was created by Don Beck and Christopher Cowan, based on the research of psychologist Clare Graves.
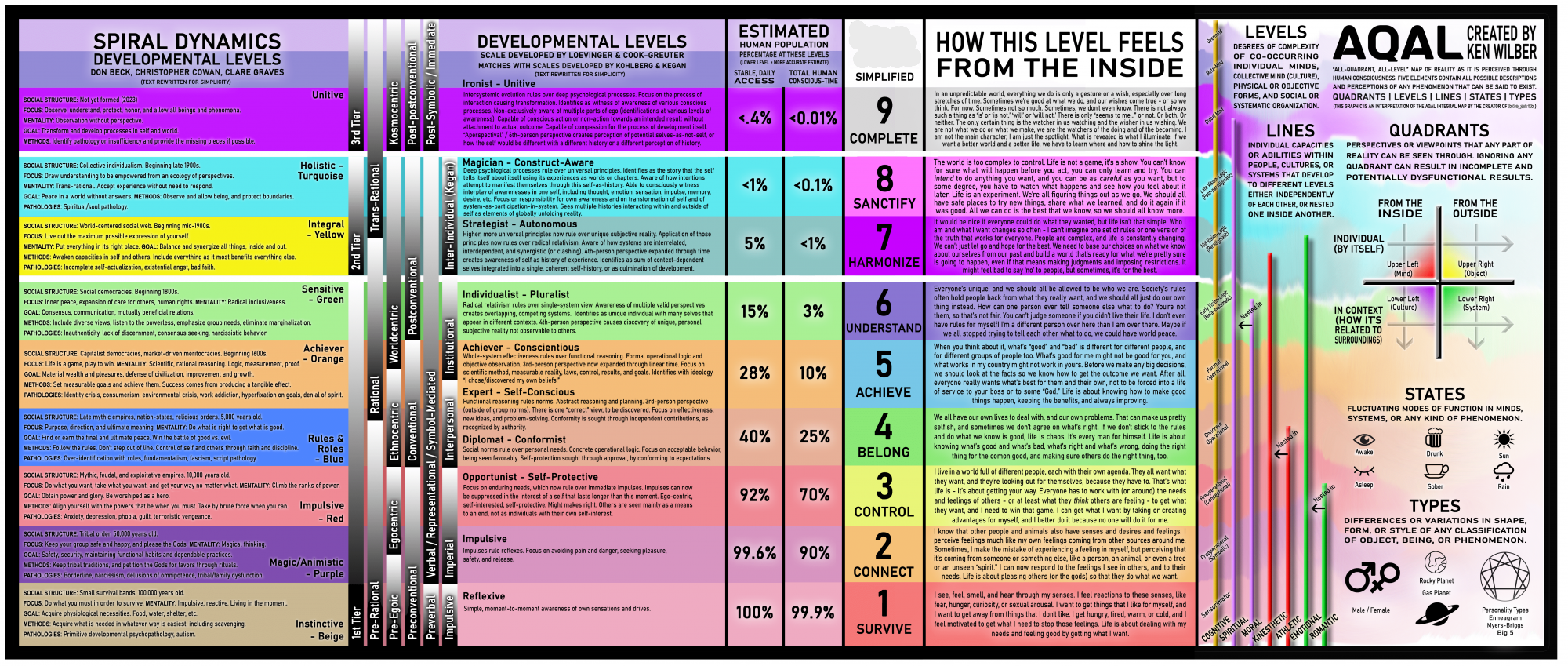
Developmental Levels
Instinctive - Beige
1st World Population
Negligible
Total Human Population
<1%
Detailed Description:
The Instinctive-Beige level is focused on immediate survival needs. Individuals at this level are primarily concerned with basic physiological necessities like food, water, warmth, and safety. They operate on instinct and automatic responses to environmental stimuli.
How this level feels: People at this level experience the world through the lens of simple, moment-to-moment awareness of own sensations and drives.
AQAL Framework
AQAL stands for "All Quadrants, All Levels" and represents Ken Wilber's integral theory framework that maps reality as it is perceived through human consciousness.
What is AQAL?
AQAL is a comprehensive map of human experience and reality developed by philosopher Ken Wilber. It integrates the insights from hundreds of disciplines into a coherent framework that can be applied to virtually any field of human endeavor.
The framework helps us understand the complexity of reality by organizing it into five key elements: Quadrants, Levels, Lines, States, and Types. This comprehensive approach allows us to see the whole picture rather than just fragments.
Relationship to Spiral Dynamics
Spiral Dynamics provides a model of how human consciousness evolves through distinct stages or "memes." Ken Wilber incorporated Spiral Dynamics into his AQAL framework, particularly in the "Levels" component.
While Spiral Dynamics focuses primarily on the evolution of values and worldviews, AQAL expands this to include multiple dimensions of reality and experience, creating a more comprehensive map of human development and reality.
The quadrants represent the four fundamental perspectives through which we can view reality:
- ULUpper Left (Interior-Individual): Subjective experience, consciousness, intentions
- URUpper Right (Exterior-Individual): Objective behaviors, brain, organism
- LLLower Left (Interior-Collective): Intersubjective culture, shared values, worldviews
- LRLower Right (Exterior-Collective): Interobjective systems, social structures, environment
Each quadrant represents a valid perspective that cannot be reduced to the others. A comprehensive understanding requires including all four perspectives.
Interior-Individual (UL)
The "I" perspective - subjective experience
Examples:
- Thoughts and feelings
- Personal values and beliefs
- Intentions and motivations
- Spiritual experiences
Disciplines:
- Psychology
- Meditation
- Phenomenology
Exterior-Individual (UR)
The "It" perspective - objective behaviors
Examples:
- Physical body and brain
- Observable behaviors
- Skills and actions
- Biological processes
Disciplines:
- Neuroscience
- Behavioral science
- Medicine
Interior-Collective (LL)
The "We" perspective - intersubjective culture
Examples:
- Shared values and meanings
- Cultural norms and ethics
- Collective worldviews
- Group identity
Disciplines:
- Cultural anthropology
- Ethics
- Hermeneutics
Exterior-Collective (LR)
The "Its" perspective - interobjective systems
Examples:
- Social systems and institutions
- Economic structures
- Ecosystems
- Technology and infrastructure
Disciplines:
- Systems theory
- Economics
- Ecology
Practical Applications of AQAL
Personal Development
AQAL provides a comprehensive map for personal growth, helping individuals:
- Identify their current developmental levels across different lines
- Recognize imbalances in development
- Create targeted practices for growth
- Integrate shadow elements
- Understand and work with different states of consciousness
Organizational Development
Organizations can use AQAL to:
- Assess organizational culture and structures
- Design more comprehensive change initiatives
- Address all four quadrants in transformation efforts
- Understand developmental diversity in teams
- Create more inclusive and effective leadership approaches
Social Change
AQAL offers insights for addressing complex social issues by:
- Recognizing the need for solutions at all levels and in all quadrants
- Understanding developmental differences in values and worldviews
- Creating more inclusive approaches to social challenges
- Designing interventions that address both interior and exterior dimensions
- Facilitating communication across developmental divides